PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer用法
一、PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的继承体系
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer位于**org.springframework.beans.factory.config** 包下,它的继承体系如下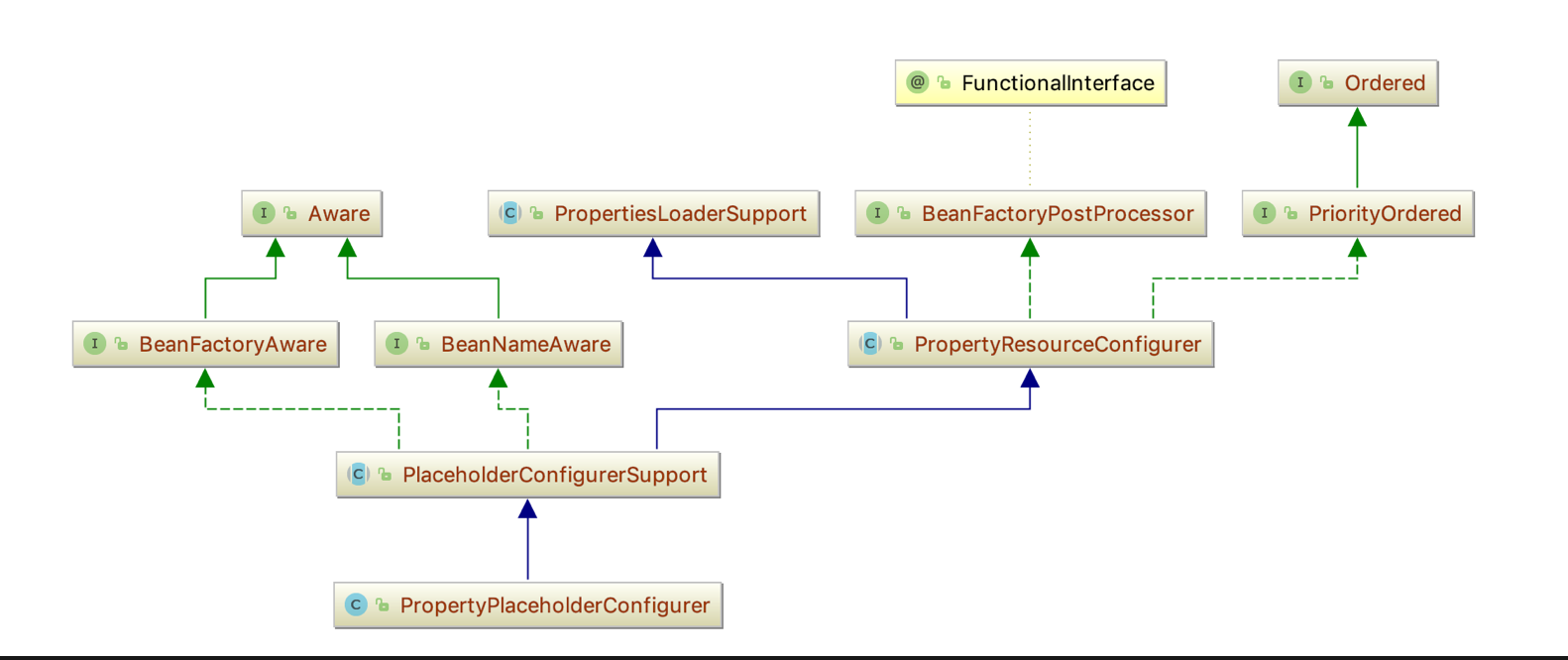

PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 直接继承于PlaceholderConfigurerSupport,它的已知实现类只有一个
PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer
二、PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的基本概念
源自JavaDoc: PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 是 **PlaceholderConfigurerSupport** 的一个子类,用来解析${…} 占位符的,可以使用setLocation和setProperties设置系统属性和环境变量。从Spring3.1 开始,**PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer**应优先与此实现,通过使用Spring3.1 中的 **Environment**和 **PropertySource**机制, 使它的灵活性更强。
但是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer却适用如下情况:当 spring-context 模块不可用的时候,使用**BeanFactory**的API 而不是**ApplicationContext**的API。现有配置使用**setSystemPropertiesMode** 和 **setSystemPropertiesModeName**属性,建议用户不要使用这些设置, 而是使用容器的**Environment**属性;在Spring3.1 之前,<context:property-placeholder/>命名空间保存了PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的实例,如果使用spring-context-3.0 xsd的定义的话,仍然会这样做。也就是说,即使使用Spring 3.1,您也可以通过命名空间保留PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer; 只是不更新schemaLocation 并继续使用3.0 XSD。
三、PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的基本使用
- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer是个bean工厂后置处理器的实现,也就是
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的一个实现。PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer可以将上下文(配置文 件)中的属性值放在另一个单独的标准java Properties文件中去。在XML文件中用${…}替换指定的properties文件中的值。这样的话,只需要对properties文件进 行修改,而不用对xml配置文件进行修改。 - 在Spring中,使用PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer可以在XML配置文件中加入外部属性文件
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 引入外部属性文件
- 定义一个properties 属性文件
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sys
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456这是一个最基本的配置数据库连接的设置,前缀统一使用jdbc来命名
- 定义xml用来获取上面properties中的内容
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>database.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
</beans>通过给PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 设置一个bean,指定
的名称为location,指定value值就能够引入外部配置文件,然后就能够通过${jdbc.key} 来获取properties 中的值
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 引入多个属性文件
- 再来定义一个encoding.properties
file.encoding=utf-8
file.name=encoding- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 引入多个属性文件比较简单,需要把location -> locations ,然后直接指定一个list 就能够引入
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>database.properties</value>
<value>encoding.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>- 这样,一个简单的数据源就设置完毕了。可以看出:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer起的作用就是将占位符指向的数据库配置信息放在bean中定义的工具。
- 查看源代码,可以发现,locations属性定义在PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的祖父类 PropertiesLoaderSupport中,而location只有 setter方法。类似于这样的配置,在spring的源程序中很常见的。PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer如果在指定的Properties文件中找不到你想使用的属性,它还会在Java的System类属性中查找。我们可以通过System.setProperty(key, value)或者java中通过-Dnamevalue来给Spring配置文件传递参数。
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的替代方案
正如PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer基本概念中提到的,Spring可以使用<context:property-placeholder/> 作为PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的替代方案,代码如下 <!-- 指定单个properties -->
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="database.properties" />-->
<!-- 指定多个properties-->
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:*.properties"/>-->
<!--<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:database.properties, classpath:encoding.properties"/>-->
<!-- 指定配置文件加载顺序-->
<context:property-placeholder order="0" location="database.properties" />
<context:property-placeholder order="1" location="encoding.properties" />四、自定义PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
- 自定义一个SubPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 继承自PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
public class SubPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer extends PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer {
private static Map<String, String> ctxPropertiesMap;
@Override
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props) throws BeansException {
// 调用父类PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的构造器
super.processProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, props);
// 遍历配置文件的key,Properties 对象就是导入的配置文件
Enumeration<?> enumeration = props.propertyNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(enumeration.nextElement());
}
ctxPropertiesMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
String keyStr = key.toString();
String value = props.getProperty(keyStr);
ctxPropertiesMap.put(keyStr, value);
}
}
public static String getProperty(String name){
return ctxPropertiesMap.get(name);
}
}- 需要引入这个自定义的SubPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
<bean id="propertyPlaceholderConfigurer" class="com.cxuan.spring.common.SubPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>database.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>如何启动呢?其实引入的SubPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 就能够随着Spring加载配置文件而被加载。
直接定义main方法,用ClassPathXmlApplicayionContext引入任意的配置文件即可。

